What is usability?
Definition (ISO 9241-11)
Usability is the extent to which a product can be used by specific users in a specific context of use in order to achieve defined goals effectively, efficiently and satisfactorily.
Usability is a key quality feature of interactive systems. It describes how well a user can interact with a product in order to achieve their goals - without unnecessary hurdles or frustration.
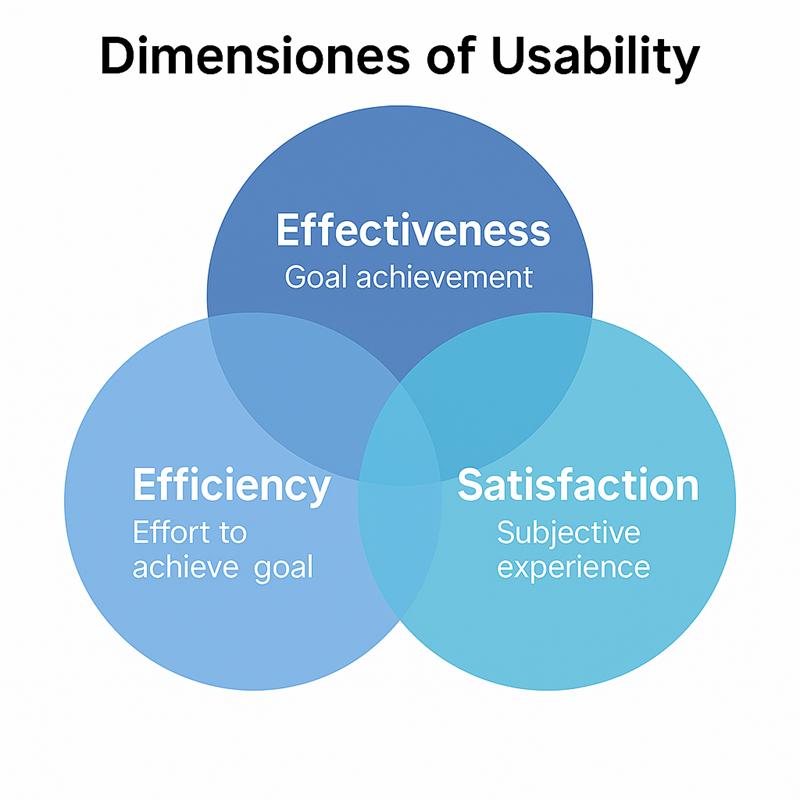
The three dimensions of usability
1. Effectiveness
The extent to which users achieve their goals completely and correctly.
Example: Is an online form filled out and sent correctly?
2. Efficiency
Effort in relation to target achievement.
Example: How many steps, clicks or thought processes does a user need to complete a task?
3. Satisfaction
Subjective experience during use (e.g. confidence, enjoyment, freedom from stress).
Example: How pleasant does a user find the operation of an app?
Usability ≠ User Experience (UX)
Usability is a sub-area of the more comprehensive User Experience (UX).
| Usability | User Experience |
|---|---|
| Focus on task fulfillment | Focus on holistic experience |
| Focused on efficiency, freedom from errors | Including emotion, trust, brand perception |
| Short-term use | Also before and after use |
Why is Usability Important?
- Economical: Good usability reduces support costs and increases conversions.
- Psychological: It promotes cognitive relief, motivation and trust.
- Ethical: It prevents frustration, errors and potential risks of use.
- Normative: It is part of many standards (e.g. ISO 9241, EN 301 549).
Conclusion
Usability is more than just “ease of use” - it is a measurable, designable characteristic of interactive systems that directly influences the achievement of objectives, workload and user satisfaction.
It is a prerequisite for good UX - but not the same as it.
Further Reading
- ISO 9241-11:2018
- Jakob Nielsen’s Usability Heuristics](https://www.nngroup.com/articles/ten-usability-heuristics/)
Frequently asked questions (FAQ)
What does usability mean?
Which three criteria define usability?
How is usability different from UX?
Why is usability important?
How can you measure usability?
Is usability regulated by standards?
Are there alternative spellings?
Last modified: 21 December 2025
